How packet travel through the switch and what is VLAN tag?
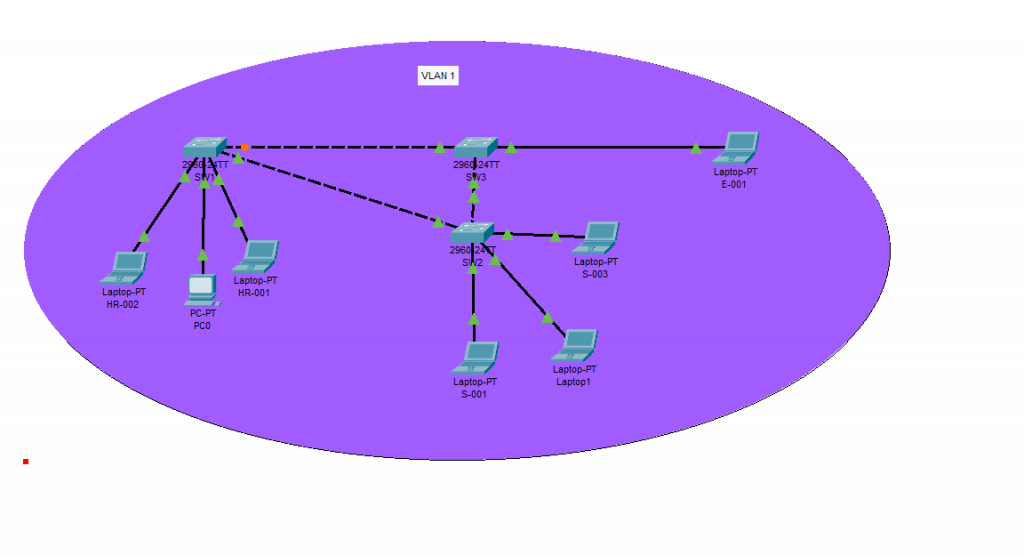
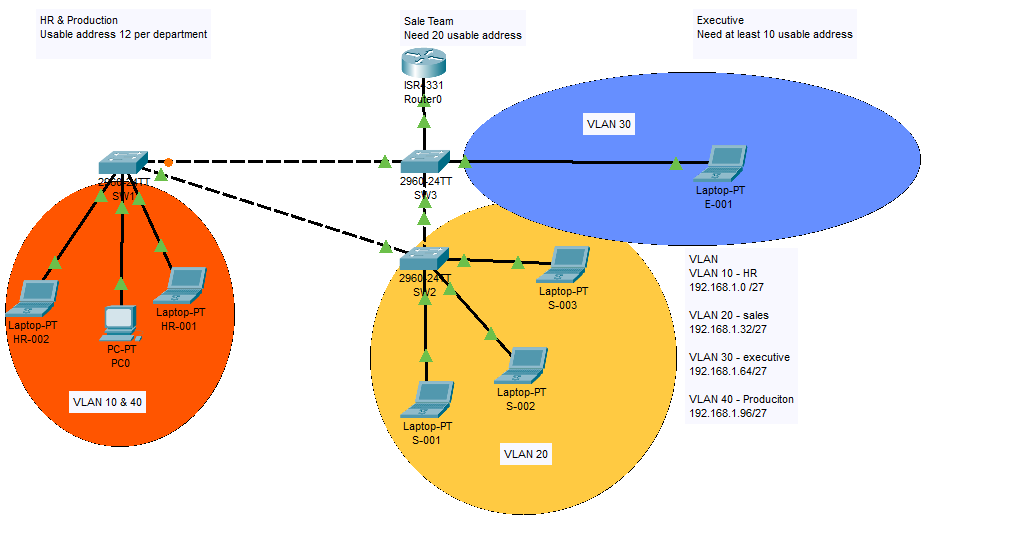
When we get a switch out of the box. We know that plug in the cable and the switch it will up and running, also by default the all those port is VLAN 1. That mean it is only one Network in this image figure 1.1 . I have set this whole Network belong to ” 192.168.1.0/24″.
______________________________
How the packet Travel in this Network
Now When PC HR-002 from the left send a ping to PC E-001 to the Right. We will use Packet Tracer simulation to see what will happen.
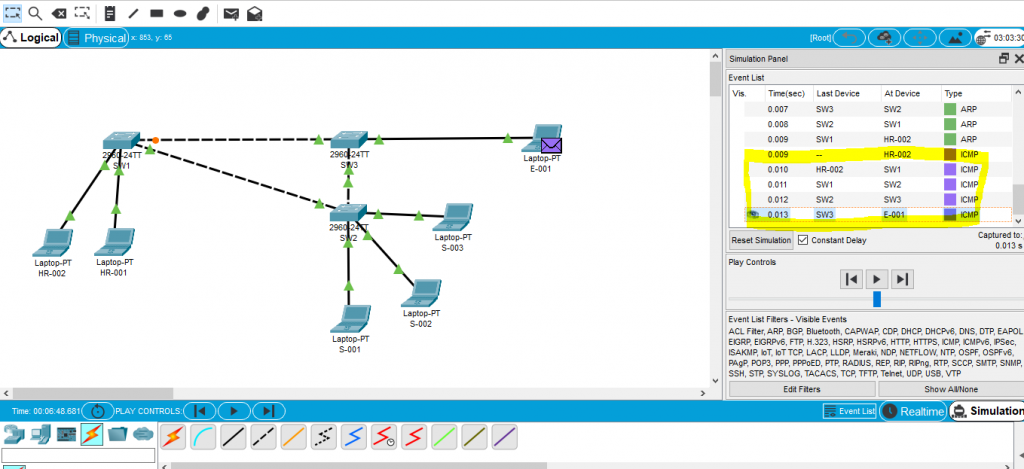
- When PC HR-002 send a ping to PC E-001. As PC doesn’t know where is other’s PC location. So it will send ARP instead of ICMP. When the ARP packet arrive SW1, SW1 doesn’t know where it belong too. SO SW1 will basically just flood this traffic to all Ports, except the incoming Ports.
- When this Packet arrive SW2 & 3, they flood all the ports as well. This is what generally switch does.
- Once both PC know where they are, then they will start sending ICMP with each other, per the image capture below “Figure 2.1”
______________________________ ______________________________
What if we put VLAN in this network, what is VLAN tag purpose ?
Now we have few departments such as Sales, HR, Production & Executive. We will need to add 4 VLAN that belong these Department. Also we are using Cisco 2960 switch here, it is a Layer 2 switch, It only read MAC address. We need to add a router or Use L3 switch instead in order to achieve inner VLAN.
On Figure 3.1, we can see which VLAN belong which network.
______________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________
PING under VLAN Network
Without VLAN, on figure 2.1. Switches will just flood all the port except from incoming port. That will increase switches processing workload, as keep sending packet or keep dropping packet which cost CPU.
After we implement VLAN, Now the picture looks more nice. 3 different colour circle on figure 5.1 which belong to different VLAN.
- Now what we will do, From VLAN 20 PC ping to VLAN 10 PC.
- Packet will go to Default Gateway Router First, Router then will tell what is the destination VLAN number
- When ARP packet reach SW1, SW1 base on the receive Packet VLAN, ONLY BOARDCAST to that VLAN
- Image on 5.1, you can see. SW1 only send packet to HR-001 & HR-002. But not PC0 ( PC0 is belong VLAN40 Production)
____________________________ ______________________________ ______________________________ ____________________________
VLAN TAGS
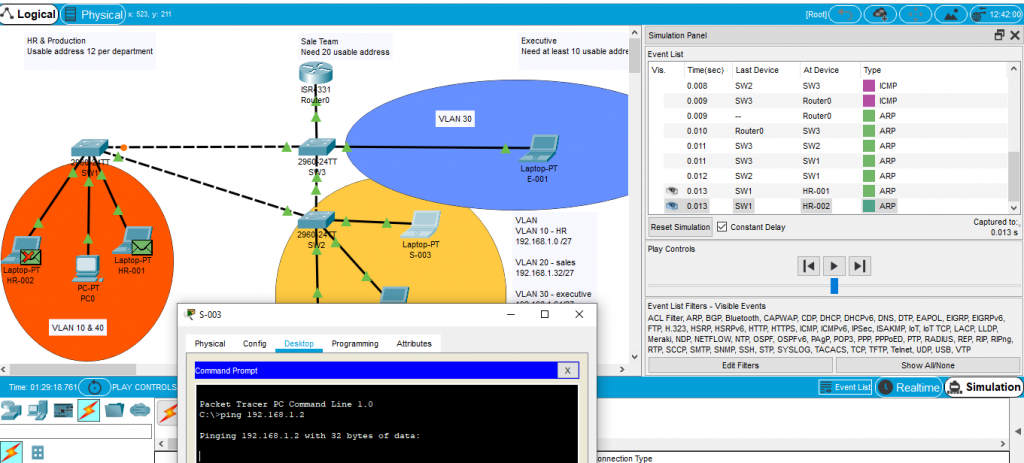
How can a switch smart enough to only read mac-address, but smart enough to read VLAN? On Packet Tracer, got a function of Simulation at right hand a bit bottom. In this section, normally wireshark will do capture network packet, Simulation can do it too.
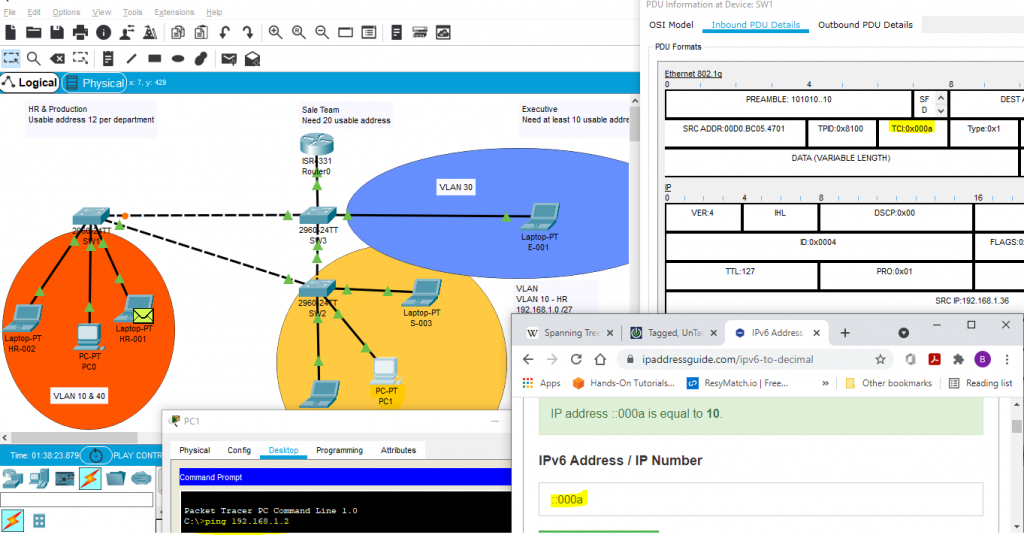
If you open the right packet, we will see so much information. Information is separated by different Layer base on OSI model. Vlan is Layer 2, you can find those information at the top “Ethernet 802.1g” .
In this layer, we can see what is sources mac address, what is destination mac-address, also VLAN tags.
- on figure 4.1, we can see this packet is belong to VLAN 10. On TCI which I already highlighted, Value is 0x000a. When you turn this to Decimal , Giving you a value 10. It is VLAN 10
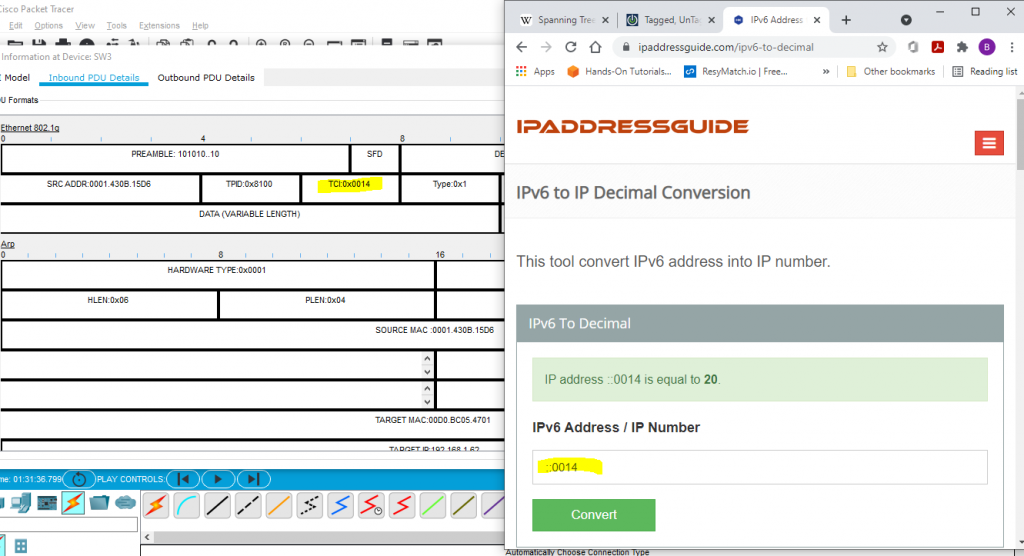
- on figure 4.2, On TCI which I already highlighted, Value is 0x0014. When you turn this to Decimal , Giving you a value 10. It is VLAN 20